OCTOBER Foreign Body Ingestion – Hima Khamar
FOREIGN BODY INGESTION
By: Hima Khamar M.D., PGY3
HISTORY
WITNESSED or UNWITNESSED
Time of ingestion
Description of object: Size, Shape, Length, Width Sharp end, similar object for comparison
Last meal time
History of GI anomaly, surgery or disease
Symptoms:
FB sensation
Refusing oral intake
Drooling, dysphagia, gagging
Choking or coughing with PO intake
Respiratory symptoms: Stridor, Hoarseness
Chest pain
Abdominal pain, vomiting (signs of perforation, obstruction)
GI Bleeding
PHYSICAL EXAM
Vital signs
Drooling, oral lesions
Tripod position
Neck crepitus, stridor
Wheezing, unequal breath sounds
Check ears and nose, especially if FB not confirmed on X-ray
Signs suggesting acute abdomen
IMAGING TIPS
AP and lateral view of chest, neck, and abdomen
Flat object location on AP:
-Esophagus: Coin appears circular
-Trachea: Coin appears as a slit
Batteries:
-Double ring on AP view
-Step-off between the anode and cathode on lateral view
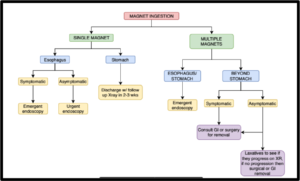
Magnets:
-Difficult to reliably distinguish single from multiple magnets
Non-radiopaque FB:
-Avoid GI contrast studies for suspected esophageal FBs: May obscure visualization on endoscopy and also increases the risk of aspiration if there is an esophageal FB
-Endoscopy favored
-CT scan may be considered in special circumstances
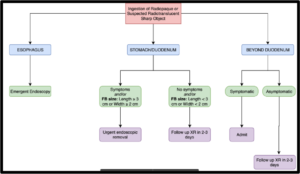
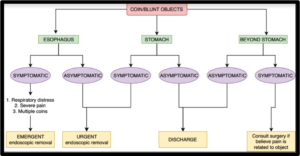
WHO NEEDS ENDOSCOPY & WHEN
| EMERGENT | URGENT | NON-URGENT |
| Esophageal location -Button battery – NO DELAY -Obstructive symptoms -Respiratory distress -Significant pain -Sharp pointed objects -Multiple magnetsStomach location -Multiple magnets |
Esophageal location -Minimal symptoms -Sharp longer objects in stomach with no symptoms |
Stomach location – FB > 2cm wide – FB > 5cm long |
BUTTON BATTERY INGESTION
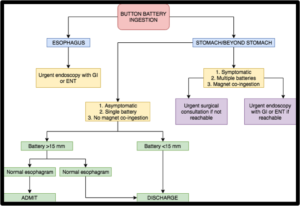
Button Battery Facts
-Serious burns can occur within 2 hrs of ingestion
-Symptoms may be delayed
-If mucosal injury is present after removal, observe for delayed complications (esophageal perforation, TEF, vocal cord paralysis, tracheal stenosis, mediastinitis, aspiration pneumonia, perforation into a large vessel)
-Complications may be delayed weeks, months
-Lithium cell batteries are most frequently involved in esophageal injuries
-Determination of battery diameter prior to removal or passage is unlikely in at least 40% of cases
-Assume hearing aid batteries are < 12 mm
-X-ray overestimates the diameter
Coins/Blunt Objects Facts
-Items within the stomach:
—Width > 2 cm, length > 5 cm (less likely to pass pylorus/duodenum)
—Repeat X-ray:
Within 2-3 weeks if Age < 2 yrs or Quarter
Within 1 week if Cylindrical battery
Sooner if symptomatic
Items beyond the stomach:
-Return if symptoms
Coins usually appear larger on the X-ray due to magnification
-Quarter à 24 mm
-Nickel à 21 mm
-Penny à 19 mm
-Dime à 18 mm
COINS/BLUNT OBJECTS INGESTION
MAGNETS INGESTION
RADIOPAQUE/SHARP RADIOTRANSLUSCENT OBJECT INGESTION